|
CGAL 4.14 - 2D and 3D Linear Geometry Kernel
|
|
CGAL 4.14 - 2D and 3D Linear Geometry Kernel
|
CGAL::compare_xy() CGAL::compare_xyz() CGAL::compare_x() CGAL::compare_y() CGAL::compare_yx() CGAL::compare_y_at_x() CGAL::compare_z() Functions | |
| template<typename Kernel > | |
| Comparison_result | CGAL::compare_x_at_y (const CGAL::Point_2< Kernel > &p, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h) |
compares the \( x\)-coordinates of p and the horizontal projection of p on h. More... | |
| template<typename Kernel > | |
| Comparison_result | CGAL::compare_x_at_y (const CGAL::Point_2< Kernel > &p, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h1, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h2) |
This function compares the \( x\)-coordinates of the horizontal projection of p on h1 and on h2. More... | |
| template<typename Kernel > | |
| Comparison_result | CGAL::compare_x_at_y (const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &l1, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &l2, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h) |
Let p be the intersection of lines l1 and l2. More... | |
| template<typename Kernel > | |
| Comparison_result | CGAL::compare_x_at_y (const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &l1, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &l2, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h1, const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > &h2) |
Let p be the intersection of lines l1 and l2. More... | |
| Comparison_result CGAL::compare_x_at_y | ( | const CGAL::Point_2< Kernel > & | p, |
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h | ||
| ) |
#include <CGAL/Kernel/global_functions.h>
compares the \( x\)-coordinates of p and the horizontal projection of p on h.
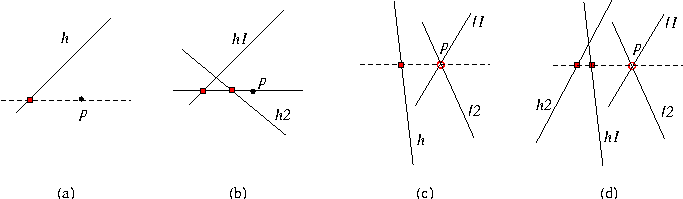
See Figure figcomparexaty (a).
h is not horizontal. | Comparison_result CGAL::compare_x_at_y | ( | const CGAL::Point_2< Kernel > & | p, |
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h1, | ||
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h2 | ||
| ) |
#include <CGAL/Kernel/global_functions.h>
This function compares the \( x\)-coordinates of the horizontal projection of p on h1 and on h2.
See Figure figcomparexaty (b).
h1 and h2 are not horizontal. | Comparison_result CGAL::compare_x_at_y | ( | const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | l1, |
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | l2, | ||
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h | ||
| ) |
#include <CGAL/Kernel/global_functions.h>
Let p be the intersection of lines l1 and l2.
This function compares the \( x\)-coordinates of p and the horizontal projection of p on h. See Figure figcomparexaty (c).
l1 and l2 intersect and are not horizontal; h is not horizontal. | Comparison_result CGAL::compare_x_at_y | ( | const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | l1, |
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | l2, | ||
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h1, | ||
| const CGAL::Line_2< Kernel > & | h2 | ||
| ) |
#include <CGAL/Kernel/global_functions.h>
Let p be the intersection of lines l1 and l2.
This function compares the \( x\)-coordinates of the horizontal projection of p on h1 and on h2 See Figure figcomparexaty (d).
l1 and l2 intersect and are not horizontal; h1 and h2 are not horizontal.