|
CGAL 4.3 - 2D Polygon Partitioning
|
|
CGAL 4.3 - 2D Polygon Partitioning
|
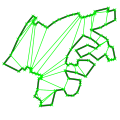
A partition of a polygon is a set of polygons such that the interiors of the polygons do not intersect and the union of the polygons is equal to the interior of the original polygon. Functions are available for partitioning planar polygons into two types of subpolygons (y-monotone polygons and convex polygons).
The function that produces a y-monotone partitioning is based on the algorithm presented in [1] which requires \( O(n \log n) \) time and \( O(n) \) space for a polygon with \( n \) vertices and guarantees nothing about the number of polygons produced with respect to the optimal number Three functions are provided for producing convex partitions. Two of these functions produce approximately optimal partitions and one results in an optimal partition, where optimal is defined in terms of the number of partition polygons. The two functions that implement approximation algorithms are guaranteed to produce no more than four times the optimal number of convex pieces. The optimal partitioning function provides an implementation of Greene's dynamic programming algorithm [2], which requires \( O(n^4) \) time and \( O(n^3) \) space to produce a convex partitioning. One of the approximation algorithms is also due to Greene [2] and requires \( O(n \log n) \) time and \( O(n) \) space to produce a convex partitioning given a y-monotone partitioning. The other approximation algorithm is a result of Hertel and Mehlhorn [3], which requires \( O(n) \) time and space to produce a convex partitioning from a triangulation of a polygon. Each of the partitioning functions uses a traits class to supply the primitive types and predicates used by the algorithms.
The assertion flags for this package use PARTITION in their names (e.g., CGAL_PARTITION_NO_POSTCONDITIONS). The precondition checks for the planar polygon partitioning functions are: counterclockwise ordering of the input vertices and simplicity of the polygon these vertices represent.
The postcondition checks are: simplicity, counterclockwise orientation, and convexity (or \( y\)-monotonicity) of the partition polygons and validity of the partition (i.e., the partition polygons are nonoverlapping and the union of these polygons is the same as the original polygon).
ConvexPartitionIsValidTraits_2IsYMonotoneTraits_2OptimalConvexPartitionTraits_2PartitionTraits_2PartitionIsValidTraits_2YMonotonePartitionIsValidTraits_2YMonotonePartitionTraits_2CGAL::Is_convex_2<Traits>CGAL::Is_vacuously_valid<Traits>CGAL::Is_y_monotone_2<Traits>CGAL::approx_convex_partition_2()CGAL::convex_partition_is_valid_2()CGAL::greene_approx_convex_partition_2()CGAL::is_y_monotone_2()CGAL::optimal_convex_partition_2()CGAL::partition_is_valid_2()CGAL::y_monotone_partition_2()CGAL::y_monotone_partition_is_valid_2() Modules | |
| Concepts | |
| Function Object Concepts | |
| Function Object Classes | |
Classes | |
| class | CGAL::Partition_is_valid_traits_2< Traits, PolygonIsValid > |
Class that derives a traits class for partition_is_valid_2() from a given traits class by defining the validity testing function object in terms of a supplied template parameter. More... | |
| class | CGAL::Partition_traits_2< R > |
| Traits class that can be used with all the 2-dimensional polygon partitioning algorithms. More... | |
Functions | |
| bool | CGAL::is_y_monotone_2 (InputIterator first, InputIterator beyond, const Traits &traits) |
determines if the sequence of points in the range [first, beyond) defines a \( y\)-monotone polygon or not. More... | |
| OutputIterator | CGAL::approx_convex_partition_2 (InputIterator first, InputIterator beyond, OutputIterator result, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
computes a partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [first, beyond) into convex polygons. More... | |
| OutputIterator | CGAL::greene_approx_convex_partition_2 (InputIterator first, InputIterator beyond, OutputIterator result, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
computes a partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [first, beyond) into convex polygons. More... | |
| OutputIterator | CGAL::optimal_convex_partition_2 (InputIterator first, InputIterator beyond, OutputIterator result, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
computes a partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [first, beyond) into convex polygons. More... | |
| OutputIterator | CGAL::y_monotone_partition_2 (InputIterator first, InputIterator beyond, OutputIterator result, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
computes a partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [first, beyond) into \( y\)-monotone polygons. More... | |
| bool | CGAL::convex_partition_is_valid_2 (InputIterator point_first, InputIterator point_beyond, ForwardIterator poly_first, ForwardIterator poly_beyond, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
determines if the polygons in the range [poly_first, poly_beyond) define a valid convex partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [point_first, point_beyond). More... | |
| bool | CGAL::partition_is_valid_2 (InputIterator point_first, InputIterator point_beyond, ForwardIterator poly_first, ForwardIterator poly_beyond, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
returns true iff the polygons in the range [poly_first, poly_beyond) define a valid partition of the polygon defined by the points in the range [point_first, point_beyond) and false otherwise. More... | |
| bool | CGAL::y_monotone_partition_is_valid_2 (InputIterator point_first, InputIterator point_beyond, ForwardIterator poly_first, ForwardIterator poly_beyond, const Traits &traits=Default_traits) |
determines if the polygons in the range [poly_first, poly_beyond) define a valid \( y\)-monotone partition of the simple, counterclockwise-oriented polygon represented by the points in the range [point_first, point_beyond). More... | |