|
CGAL 4.9.1 - 2D and 3D Linear Geometry Kernel
|
|
CGAL 4.9.1 - 2D and 3D Linear Geometry Kernel
|
#include <CGAL/Iso_cuboid_3.h>
An object c of the data type Iso_cuboid_3 is a cuboid in the Euclidean space \( \E^3\) with edges parallel to the \( x\), \( y\) and \( z\) axis of the coordinate system.
Although they are represented in a canonical form by only two vertices, namely the lexicographically smallest and largest vertex with respect to Cartesian \( xyz\) coordinates, we provide functions for "accessing" the other vertices as well.
Iso-oriented cuboids and bounding boxes are quite similar. The difference however is that bounding boxes have always double coordinates, whereas the coordinate type of an iso-oriented cuboid is chosen by the user.
Kernel::IsoCuboid_3 Creation | |
| Iso_cuboid_3 (const Point_3< Kernel > &p, const Point_3< Kernel > &q) | |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices p and q. More... | |
| Iso_cuboid_3 (const Point_3< Kernel > &p, const Point_3< Kernel > &q, int) | |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices p and q. More... | |
| Iso_cuboid_3 (const Point_3< Kernel > &left, const Point_3< Kernel > &right, const Point_3< Kernel > &bottom, const Point_3< Kernel > &top, const Point_3< Kernel > &far, const Point_3< Kernel > &close) | |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c whose minimal \( x\) coordinate is the one of left, the maximal \( x\) coordinate is the one of right, the minimal \( y\) coordinate is the one of bottom, the maximal \( y\) coordinate is the one of top, the minimal \( z\) coordinate is the one of far, the maximal \( z\) coordinate is the one of close. | |
| Iso_cuboid_3 (const Kernel::RT &min_hx, const Kernel::RT &min_hy, const Kernel::RT &min_hz, const Kernel::RT &max_hx, const Kernel::RT &max_hy, const Kernel::RT &max_hz, const Kernel::RT &hw=RT(1)) | |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices (min_hx/hw, min_hy/hw, min_hz/hw) and (max_hx/hw, max_hy/hw, max_hz/hw). More... | |
| Iso_cuboid_3 (const Bbox_3 &bbox) | |
If Kernel::RT is constructible from double, introduces an iso-oriented cuboid from bbox. | |
Operations | |
| bool | operator== (const Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel > &c2) const |
| Test for equality: two iso-oriented cuboid are equal, iff their lower left and their upper right vertices are equal. | |
| bool | operator!= (const Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel > &c2) const |
| Test for inequality. | |
| Point_3< Kernel > | vertex (int i) const |
returns the i'th vertex modulo 8 of c. More... | |
| Point_3< Kernel > | operator[] (int i) const |
returns vertex(i), as indicated in the figure below: More... | |
| Point_3< Kernel > | min () const |
returns the smallest vertex of c (= vertex(0)). | |
| Point_3< Kernel > | max () const |
returns the largest vertex of c (= vertex(7)). | |
| Kernel::FT | xmin () const |
returns smallest Cartesian \( x\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | ymin () const |
returns smallest Cartesian \( y\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | zmin () const |
returns smallest Cartesian \( z\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | xmax () const |
returns largest Cartesian \( x\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | ymax () const |
returns largest Cartesian \( y\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | zmax () const |
returns largest Cartesian \( z\)-coordinate in c. | |
| Kernel::FT | min_coord (int i) const |
returns i-th Cartesian coordinate of the smallest vertex of c. More... | |
| Kernel::FT | max_coord (int i) const |
returns i-th Cartesian coordinate of the largest vertex of c. More... | |
Predicates | |
| bool | is_degenerate () const |
c is degenerate, if all vertices are coplanar. | |
| Bounded_side | bounded_side (const Point_3< Kernel > &p) const |
returns either ON_UNBOUNDED_SIDE, ON_BOUNDED_SIDE, or the constant ON_BOUNDARY, depending on where point p is. | |
| bool | has_on_boundary (const Point_3< Kernel > &p) const |
| bool | has_on_bounded_side (const Point_3< Kernel > &p) const |
| bool | has_on_unbounded_side (const Point_3< Kernel > &p) const |
Miscellaneous | |
| Kernel::FT | volume () const |
returns the volume of c. | |
| Bbox_3 | bbox () const |
returns a bounding box containing c. | |
| Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel > | transform (const Aff_transformation_3< Kernel > &t) const |
returns the iso-oriented cuboid obtained by applying t on the smallest and the largest of c. More... | |
| CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::Iso_cuboid_3 | ( | const Point_3< Kernel > & | p, |
| const Point_3< Kernel > & | q | ||
| ) |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices p and q.
Note that the object is brought in the canonical form.
| CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::Iso_cuboid_3 | ( | const Point_3< Kernel > & | p, |
| const Point_3< Kernel > & | q, | ||
| int | |||
| ) |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices p and q.
The int argument value is only used to distinguish the two overloaded functions.
p.x()<=q.x(), p.y()<=q.y()and p.z()<=q.z(). | CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::Iso_cuboid_3 | ( | const Kernel::RT & | min_hx, |
| const Kernel::RT & | min_hy, | ||
| const Kernel::RT & | min_hz, | ||
| const Kernel::RT & | max_hx, | ||
| const Kernel::RT & | max_hy, | ||
| const Kernel::RT & | max_hz, | ||
| const Kernel::RT & | hw = RT(1) |
||
| ) |
introduces an iso-oriented cuboid c with diagonal opposite vertices (min_hx/hw, min_hy/hw, min_hz/hw) and (max_hx/hw, max_hy/hw, max_hz/hw).
hw \( \neq\) 0. | Kernel::FT CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::max_coord | ( | int | i) | const |
returns i-th Cartesian coordinate of the largest vertex of c.
| Kernel::FT CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::min_coord | ( | int | i) | const |
returns i-th Cartesian coordinate of the smallest vertex of c.
| Point_3<Kernel> CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::operator[] | ( | int | i) | const |
returns vertex(i), as indicated in the figure below:
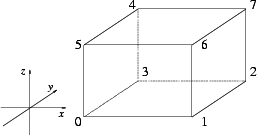
| Iso_cuboid_3<Kernel> CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::transform | ( | const Aff_transformation_3< Kernel > & | t) | const |
returns the iso-oriented cuboid obtained by applying t on the smallest and the largest of c.
| Point_3<Kernel> CGAL::Iso_cuboid_3< Kernel >::vertex | ( | int | i) | const |
returns the i'th vertex modulo 8 of c.
starting with the lower left vertex.