 |
An instance E of the data type Explorer is a decorator to explore the structure of the plane map underlying the Nef polyhedron. It inherits all topological adjacency exploration operations from Topological_explorer. Explorer additionally allows one to explore the geometric embedding.
The position of each vertex is given by a so-called extended point, which is either a standard affine point or the tip of a ray touching an infinimaximal square frame centered at the origin. A vertex v is called a standard vertex if its embedding is a standard point and non-standard if its embedding is a non-standard point. By the straightline embedding of their source and target vertices, edges correspond to either affine segments, rays or lines or are part of the bounding frame.
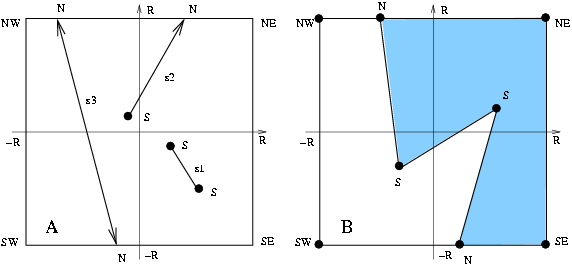
Figure 20.2: Extended geometry: standard vertices are marked by S, non-standard vertices are marked by N. A: The possible embeddings of edges: an affine segment s1, an affine ray s2, an affine line s3. B: A plane map embedded by extended geometry: note that the frame is arbitrarily large, the 6 vertices on the frame are at infinity, the two faces represent a geometrically unbounded area, however they are topologically closed by the frame edges. No standard point can be placed outside the frame.
| Explorer::Point | |
|
the point type of finite vertices.
| |
| Explorer::Ray | |
|
the ray type of vertices on the frame.
| |
Iterators, handles, and circulators are inherited from Topological_explorer.
Explorer is copy constructable and assignable. An object can be obtained via the Nef_polyhedron_2::explorer() method of Nef_polyhedron_2.