Tran Kai Frank Da, Sébastien Loriot, and Mariette Yvinec

Assume we are given a set S of points in 2D or 3D and we'd like to have something like ``the shape formed by these points.'' This is quite a vague notion and there are probably many possible interpretations, the alpha shape being one of them. Alpha shapes can be used for shape reconstruction from a dense unorganized set of data points. Indeed, an alpha shape is demarcated by a frontier, which is a linear approximation of the original shape [BB97].
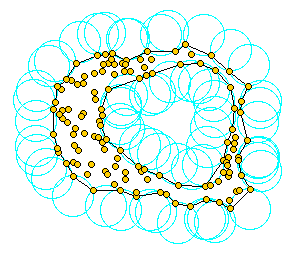
As mentioned in Edelsbrunner's and Mücke's paper [EM94], one can intuitively think of an alpha shape as the following. Imagine a huge mass of ice-cream making up the space ℝ3 and containing the points as ``hard'' chocolate pieces. Using one of those sphere-formed ice-cream spoons we carve out all parts of the ice-cream block we can reach without bumping into chocolate pieces, thereby even carving out holes in the inside (e.g. parts not reachable by simply moving the spoon from the outside). We will eventually end up with a (not necessarily convex) object bounded by caps, arcs and points. If we now straighten all ``round'' faces to triangles and line segments, we have an intuitive description of what is called the alpha shape of S. Here's an example for this process in 2D (where our ice-cream spoon is simply a circle):
Alpha shapes depend on a parameter α from which they are named. What is α in the ice-cream game? α is the squared radius of the carving spoon. A very small value will allow us to eat up all of the ice-cream except the chocolate points themselves. Thus we already see that the alpha shape degenerates to the point-set S for α → 0. On the other hand, a huge value of α will prevent us even from moving the spoon between two points since it's way too large. So we will never spoon up ice-cream lying in the inside of the convex hull of S, and hence the alpha shape for α → ∞ is the convex hull of S.1
More precisely, the definition of alpha shapes is based on an underlying triangulation that may be a Delaunay triangulation in case of basic alpha shapes or a regular triangulation (cf. 39.3) in case of weighted alpha shapes.
Let us consider the basic case with a Delaunay triangulation. We first define the alpha complex of the set of points S. The alpha complex is a subcomplex of the Delaunay triangulation. For a given value of α, the alpha complex includes all the simplices in the Delaunay triangulation which have an empty circumscribing sphere with squared radius equal or smaller than α. Here ``empty'' means that the open sphere do not include any points of S. The alpha shape is then simply the domain covered by the simplices of the alpha complex (see [EM94]).
In general, an alpha complex is a disconnected and non-pure complex: This means in particular that the alpha complex may have singular faces. For 0 ≤ k ≤ d-1, a k-simplex of the alpha complex is said to be singular if it is not a facet of a (k+1)-simplex of the complex. CGAL provides two versions of alpha shapes. In the general mode, the alpha shapes correspond strictly to the above definition. The regularized mode provides a regularized version of the alpha shapes. It corresponds to the domain covered by a regularized version of the alpha complex where singular faces are removed (See Figure 43.1 for an example).
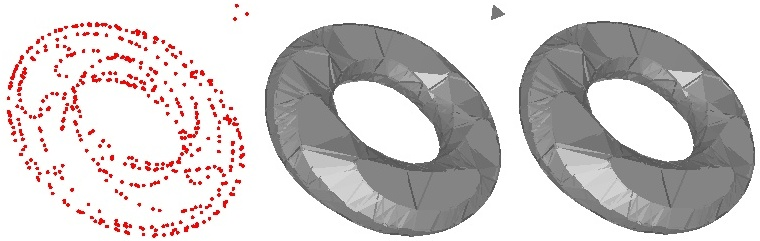
Figure 43.1: Comparison of general and regularized alpha-shape. Left: Some points are taken on the surface of a torus, three points being taken relatively far from the surface of the torus; Middle: The general alpha-shape (for a large enough alpha value) contains the singular triangle facet of the three isolated points; Right: The regularized version (for the same value of alpha) does not contains any singular facet.
The alpha shapes of a set of points S form a discrete family, even though they are defined for all real numbers α. The entire family of alpha shapes can be represented through the underlying triangulation of S. In this representation each k-simplex of the underlying triangulation is associated with an interval that specifies for which values of α the k-simplex belongs to the alpha complex. Relying on this fact, the family of alpha shapes can be computed efficiently and relatively easily. Furthermore, we can select the optimal value of α to get an alpha shape including all data points and having less than a given number of connected components. Also, the alpha-values allows to define a filtration on the faces of the triangulation of a set of points. In this filtration, the faces of the triangulation are output in increasing order of the alpha value for which they appear in the alpha complex. In case of equal alpha value lower dimensional faces are output first.
The definition is analog in the case of weighted alpha shapes. The input set is now a set of weighted points (which can be regarded as spheres) and the underlying triangulation is the regular triangulation of this set. Two spheres, or two weighted points , with centers C1, C2 and radii r1, r2 are said to be orthogonal iff C1C2 2 = r12 + r22 and suborthogonal iff C1C2 2 < r12 + r22. For a given value of α the weighted alpha complex is formed with the simplices of the regular triangulation triangulation such that there is a sphere orthogonal to the weighted points associated with the vertices of the simplex and suborthogonal to all the other input weighted points. Once again the alpha shape is then defined as the domain covered by a the alpha complex and comes in general and regularized versions.
The class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> represents the whole family of alpha shapes for a given set of points. The class includes the underlying triangulation Dt of the set, and associates to each k-face of this triangulation an interval specifying for which values of α the face belongs to the alpha complex.
The class provides functions to set and get the current α-value, as well as an iterator that enumerates the α values where the alpha shape changes.
Also the class has a filtration member function that, given an output iterator with CGAL::object as value type, outputs the faces of the triangulation according to the order of apparition in the alpha complex when alpha increases.
Finally, it provides a function to determine
the smallest value α
such that the alpha shape satisfies the following two properties
(ii) all data points are either on the boundary or in the interior
of the regularized version of the alpha shape (no singular faces).
(i) The number of components is equal or less than a given number .
The current implementation is static, that is after its construction
points cannot be inserted or removed.
The current implementation of this class is dynamic, that is after its construction
points can be inserted or removed.
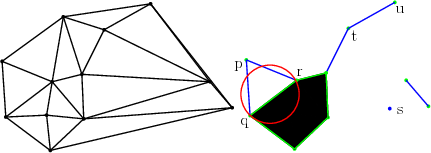
Figure 43.2: Classification of simplices, a 2D example. Left: The 2D Delaunay triangulation of a set of points; Right: Classification of simplices for a given alpha (the squared radius of the red circle). INTERIOR, REGULAR and SINGULAR simplices are depicted in black, green and blue respectively. EXTERIOR simplices are not depicted. The vertex s and the edge tu are SINGULAR since all higher dimension simplices they are incident to are EXTERIOR. The facet pqr is EXTERIOR because the squared radius of its circumscribed circle is larger than alpha.
The classes provide also output iterators to get for a given alpha value the vertices, edges, facets and cells of the different types (EXTERIOR, SINGULAR, REGULAR or INTERIOR).
We currently do not specify concepts for the underlying triangulation type. Models that work for a familly alpha-shapes are the instantiations of the classes CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3 and CGAL::Periodic_3_Delaunay_triangulation_3 (see example 43.5.6). A model that works for a fixed alpha-shape are the instantiations of the class CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3. A model that works for a weighted alpha-shape is the class CGAL::Regular_triangulation_3. The triangulation needs a geometric traits class and a triangulation data structure as template parameters.
For the class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag>, the requirements of the traits class are described in the concepts CGAL::AlphaShapeTraits_3 in the non-weighted case and CGAL::WeightedAlphaShapeTraits_3 in the weighted case. The Cgal kernels are models in the non-weighted case, and the class CGAL::Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3 is a model in the weighted case. The triangulation data structure of the triangulation has to be a model of the concept CGAL::TriangulationDataStructure_3, and it must be parameterized with vertex and cell classes, which are model of the concepts AlphaShapeVertex_3 and AlphaShapeCell_3. The package provides by default the classes CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt> and CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt>. When using CGAL::Periodic_3_Delaunay_triangulation_3 as underlying triangulation the vertex and cell classes need to be models to both AlphaShapeVertex_3 and Periodic_3TriangulationDSVertexBase_3 as well as AlphaShapeCell_3 and Periodic_3TriangulationDSCellBase_3 (see example 43.5.6).
For the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt>, the requirements of the traits class are described in the concepts CGAL::FixedAlphaShapeTraits_3 in the non-weighted case and CGAL::FixedWeightedAlphaShapeTraits_3 in the weighted case. The Cgal kernels are models in the non-weighted case, and the class CGAL::Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3 is a model in the weighted case. The triangulation data structure of the triangulation has to be a model of the concept CGAL::TriangulationDataStructure_3, and it must be parameterized with vertex and cell classes, which are model of the concepts FixedAlphaShapeVertex_3 and FixedAlphaShapeCell_3. The package provides models CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt> and CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt>, respectively.
The class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> represents the whole family of alpha shapes for a given set of points while the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt> represents only one alpha shape (for a fixed alpha). When using the same kernel, CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt> being a lighter version, it is naturally much more efficient when the alpha-shape is needed for a single given value of alpha. In addition note that the class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> requires constructions (squared radius of simplices) while the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt> uses only predicates. This implies that a certified construction of one (several) alpha-shape, using the CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> requires a kernel with exact predicates and exact constructions (or setting ExactAlphaComparisonTag to CGAL::Tag_true) while using a kernel with exact predicates is sufficient for the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt>. This makes the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt> even more efficient in this setting. In addition, note that the Fixed version is the only of the two that supports incremental insertion and removal of points.
We give the time spent while computing the alpha shape of a protein (considered as a set of weighted points) featuring 4251 atoms (using gcc 4.3 under Linux with -O3 and -DNDEBUG flags, on a 2.27GHz Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5520 CPU): Using CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel, building the regular triangulation requires 0.09s, then the class CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Dt> required 0.05s while the class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> requires 0.35s if ExactAlphaComparisonTag is CGAL::Tag_false (and 0.70s with CGAL::Tag_true). Using CGAL::Exact_predicates_exact_constructions_kernel, building the regular triangulation requires 0.19s and then the class CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Dt,ExactAlphaComparisonTag> requires 0.90s.
This example builds a basic alpha shape using a Delaunay triangulation as underlying triangulation.
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_alpha_shapes_3.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <list>
#include <cassert>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Gt;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt> Fb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<Vb,Fb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3<Gt,Tds> Triangulation_3;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Triangulation_3> Alpha_shape_3;
typedef Gt::Point_3 Point;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Alpha_iterator Alpha_iterator;
int main()
{
std::list<Point> lp;
//read input
std::ifstream is("./data/bunny_1000");
int n;
is >> n;
std::cout << "Reading " << n << " points " << std::endl;
Point p;
for( ; n>0 ; n--) {
is >> p;
lp.push_back(p);
}
// compute alpha shape
Alpha_shape_3 as(lp.begin(),lp.end());
std::cout << "Alpha shape computed in REGULARIZED mode by default"
<< std::endl;
// find optimal alpha value
Alpha_iterator opt = as.find_optimal_alpha(1);
std::cout << "Optimal alpha value to get one connected component is "
<< *opt << std::endl;
as.set_alpha(*opt);
assert(as.number_of_solid_components() == 1);
return 0;
}
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_alpha_shapes_with_fast_location_3.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <list>
#include <cassert>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<K> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<K> Fb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<Vb,Fb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3<K,Tds,CGAL::Fast_location> Delaunay;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Delaunay> Alpha_shape_3;
typedef K::Point_3 Point;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Alpha_iterator Alpha_iterator;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::NT NT;
int main()
{
Delaunay dt;
std::ifstream is("./data/bunny_1000");
int n;
is >> n;
Point p;
std::cout << n << " points read" << std::endl;
for( ; n>0 ; n--) {
is >> p;
dt.insert(p);
}
std::cout << "Delaunay computed." << std::endl;
// compute alpha shape
Alpha_shape_3 as(dt);
std::cout << "Alpha shape computed in REGULARIZED mode by defaut."
<< std::endl;
// find optimal alpha values
Alpha_shape_3::NT alpha_solid = as.find_alpha_solid();
Alpha_iterator opt = as.find_optimal_alpha(1);
std::cout << "Smallest alpha value to get a solid through data points is "
<< alpha_solid << std::endl;
std::cout << "Optimal alpha value to get one connected component is "
<< *opt << std::endl;
as.set_alpha(*opt);
assert(as.number_of_solid_components() == 1);
return 0;
}
The following examples build a weighted alpha shape requiring a regular triangulation as underlying triangulation. The alpha shape is built in GENERAL mode.
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_weighted_alpha_shapes_3.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Regular_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <list>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3<K> Gt;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt> Fb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<Vb,Fb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Regular_triangulation_3<Gt,Tds> Triangulation_3;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Triangulation_3> Alpha_shape_3;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Cell_handle Cell_handle;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Vertex_handle Vertex_handle;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Facet Facet;
typedef Alpha_shape_3::Edge Edge;
typedef Gt::Weighted_point Weighted_point;
typedef Gt::Bare_point Bare_point;
int main()
{
std::list<Weighted_point> lwp;
//input : a small molecule
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 1, -1, -1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point(-1, 1, -1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point(-1, -1, 1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 1, 1, 1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 2, 2, 2), 1));
//build alpha_shape in GENERAL mode and set alpha=0
Alpha_shape_3 as(lwp.begin(), lwp.end(), 0, Alpha_shape_3::GENERAL);
//explore the 0-shape - It is dual to the boundary of the union.
std::list<Cell_handle> cells;
std::list<Facet> facets;
std::list<Edge> edges;
as.get_alpha_shape_cells(std::back_inserter(cells),
Alpha_shape_3::INTERIOR);
as.get_alpha_shape_facets(std::back_inserter(facets),
Alpha_shape_3::REGULAR);
as.get_alpha_shape_facets(std::back_inserter(facets),
Alpha_shape_3::SINGULAR);
as.get_alpha_shape_edges(std::back_inserter(edges),
Alpha_shape_3::SINGULAR);
std::cout << " The 0-shape has : " << std::endl;
std::cout << cells.size() << " interior tetrahedra" << std::endl;
std::cout << facets.size() << " boundary facets" << std::endl;
std::cout << edges.size() << " singular edges" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Same example as previous but using a fixed value of alpha.
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_fixed_weighted_alpha_shapes_3.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Regular_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Fixed_alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Fixed_alpha_shape_vertex_base_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Fixed_alpha_shape_cell_base_3.h>
#include <list>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Regular_triangulation_euclidean_traits_3<K> Gt;
typedef CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt> Fb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<Vb,Fb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Regular_triangulation_3<Gt,Tds> Triangulation_3;
typedef CGAL::Fixed_alpha_shape_3<Triangulation_3> Fixed_alpha_shape_3;
typedef Fixed_alpha_shape_3::Cell_handle Cell_handle;
typedef Fixed_alpha_shape_3::Vertex_handle Vertex_handle;
typedef Fixed_alpha_shape_3::Facet Facet;
typedef Fixed_alpha_shape_3::Edge Edge;
typedef Gt::Weighted_point Weighted_point;
typedef Gt::Bare_point Bare_point;
int main()
{
std::list<Weighted_point> lwp;
//input : a small molecule
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 1, -1, -1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point(-1, 1, -1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point(-1, -1, 1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 1, 1, 1), 4));
lwp.push_back(Weighted_point(Bare_point( 2, 2, 2), 1));
//build one alpha_shape with alpha=0
Fixed_alpha_shape_3 as(lwp.begin(), lwp.end(), 0);
//explore the 0-shape - It is dual to the boundary of the union.
std::list<Cell_handle> cells;
std::list<Facet> facets;
std::list<Edge> edges;
as.get_alpha_shape_cells(std::back_inserter(cells),
Fixed_alpha_shape_3::INTERIOR);
as.get_alpha_shape_facets(std::back_inserter(facets),
Fixed_alpha_shape_3::REGULAR);
as.get_alpha_shape_facets(std::back_inserter(facets),
Fixed_alpha_shape_3::SINGULAR);
as.get_alpha_shape_edges(std::back_inserter(edges),
Fixed_alpha_shape_3::SINGULAR);
std::cout << " The 0-shape has : " << std::endl;
std::cout << cells.size() << " interior tetrahedra" << std::endl;
std::cout << facets.size() << " boundary facets" << std::endl;
std::cout << edges.size() << " singular edges" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
On some platforms, the alpha shapes of the set of points of this example cannot be computed when using a traits with inexact constructions. To be able to compute them with a traits with inexact constructions, the tag ExactAlphaComparisonTag is set to CGAL::Tag_true.
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_alpha_shapes_exact_alpha.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <list>
#include <cassert>
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Gt;
typedef CGAL::Tag_true Alpha_cmp_tag;
//We use CGAL::Default to skip the complete declaration of base classes
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<Gt,CGAL::Default,Alpha_cmp_tag> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<Gt,CGAL::Default,Alpha_cmp_tag> Fb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<Vb,Fb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Delaunay_triangulation_3<Gt,Tds> Triangulation_3;
//Alpha shape with ExactAlphaComparisonTag set to true (note that the tag is also
//set to true for Vb and Fb)
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<Triangulation_3,Alpha_cmp_tag> Alpha_shape_3;
typedef Gt::Point_3 Point;
int main()
{
//Set of points for which the alpha shapes cannot be computed with
//a floating point alpha value (on certain platforms)
std::list<Point> lp;
lp.push_back(Point(49.2559,29.1767,6.7723));
lp.push_back(Point(49.3696,31.4775,5.33777));
lp.push_back(Point(49.4264,32.6279,4.6205));
lp.push_back(Point(49.3127,30.3271,6.05503));
// compute alpha shape
Alpha_shape_3 as(lp.begin(),lp.end(),0,Alpha_shape_3::GENERAL);
return 0;
}
The following example shows how to use the periodic Delaunay triangulation (Chapter 41) as underlying triangulation for the alpha shape computation.
In order to define the original domain and to benefit from the built-in heuristic optimizations of the periodic Delaunay triangulation computation it is recommended to first construct the triangulation and then construct the alpha shape from it. The alpha shape constructor that takes a point range can be used as well but in this case the original domain cannot be specified and the default unit cube will be chosen and no optimizations will be used.
It is also recommended to switch the triangulation to 1-sheeted covering if possible. Note that a periodic triangulation in 27-sheeted covering space is degenerate. In this case an exact constructions kernel needs to be used to compute the alpha shapes. Otherwise the results will suffer from round-off problems.
File: examples/Alpha_shapes_3/ex_periodic_alpha_shapes_3.cpp
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Periodic_3_triangulation_traits_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Periodic_3_Delaunay_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Alpha_shape_3.h>
#include <CGAL/Random.h>
#include <CGAL/point_generators_3.h>
// Traits
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel K;
typedef CGAL::Periodic_3_triangulation_traits_3<K> PK;
// Vertex type
typedef CGAL::Periodic_3_triangulation_ds_vertex_base_3<> DsVb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_vertex_base_3<PK,DsVb> Vb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_vertex_base_3<PK,Vb> AsVb;
// Cell type
typedef CGAL::Periodic_3_triangulation_ds_cell_base_3<> DsCb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_cell_base_3<PK,DsCb> Cb;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_cell_base_3<PK,Cb> AsCb;
typedef CGAL::Triangulation_data_structure_3<AsVb,AsCb> Tds;
typedef CGAL::Periodic_3_Delaunay_triangulation_3<PK,Tds> P3DT3;
typedef CGAL::Alpha_shape_3<P3DT3> Alpha_shape_3;
typedef PK::Point_3 Point;
int main()
{
typedef CGAL::Creator_uniform_3<double, Point> Creator;
CGAL::Random random(7);
CGAL::Random_points_in_cube_3<Point, Creator> in_cube(1, random);
std::vector<Point> pts;
// Generating 1000 random points
for (int i=0 ; i < 1000 ; i++) {
Point p = *in_cube++;
pts.push_back(p);
}
// Define the periodic cube
P3DT3 pdt(PK::Iso_cuboid_3(-1,-1,-1,1,1,1));
// Heuristic for inserting large point sets (if pts is reasonably large)
pdt.insert(pts.begin(), pts.end(), true);
// As pdt won't be modified anymore switch to 1-sheeted cover if possible
if (pdt.is_triangulation_in_1_sheet()) pdt.convert_to_1_sheeted_covering();
std::cout << "Periodic Delaunay computed." << std::endl;
// compute alpha shape
Alpha_shape_3 as(pdt);
std::cout << "Alpha shape computed in REGULARIZED mode by default."
<< std::endl;
// find optimal alpha values
Alpha_shape_3::NT alpha_solid = as.find_alpha_solid();
Alpha_shape_3::Alpha_iterator opt = as.find_optimal_alpha(1);
std::cout << "Smallest alpha value to get a solid through data points is "
<< alpha_solid << std::endl;
std::cout << "Optimal alpha value to get one connected component is "
<< *opt << std::endl;
as.set_alpha(*opt);
assert(as.number_of_solid_components() == 1);
return 0;
}
| 1 | ice cream, ice cream!!! The wording of this introductory paragraphs is borrowed from Kaspar Fischer's `` Introduction to Alpha Shapes'' which can be found at http://people.inf.ethz.ch/fischerk/pubs/as.pdf. The picture has been taken from Walter Luh's homepage at http://www.stanford.edu/&wtilde;luh/cs448b/alphashapes.html. |