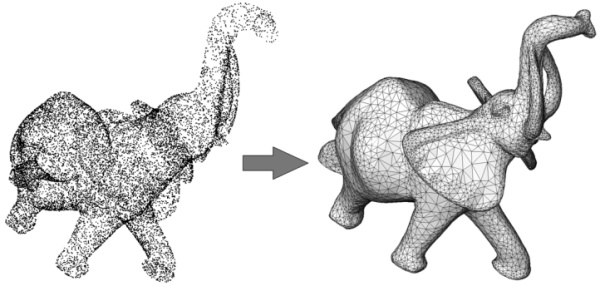
Figure 49.1: Poisson surface reconstruction. Left: 17K points sampled on the statue of an elephant with a Minolta laser scanner. Right: reconstructed surface mesh.
Pierre Alliez, Laurent Saboret, Gaël Guennebaud
| 49.1 | Introduction | ||||
| 49.2 | Common Reconstruction Pipeline | ||||
| 49.3 | Poisson | ||||
| 49.3.1 Interface | |||||
| 49.3.2 Example | |||||
| 49.4 | Contouring | ||||
| 49.5 | Output | ||||
| 49.6 | Case Studies | ||||
| 49.6.1 Ideal Conditions | |||||
| 49.6.2 Degraded Conditions | |||||
This Cgal component implements a surface reconstruction method which takes as input point sets with oriented normals and computes an implicit function. We assume that the input points contain no outliers and little noise. The output surface mesh is generated by extracting an isosurface of this function with the Cgal Surface Mesh Generator [RY07] or potentially with any other surface contouring algorithm.

Figure 49.1: Poisson surface reconstruction. Left: 17K points sampled on the statue of an elephant with a Minolta laser scanner. Right: reconstructed surface mesh.
More specifically, the core surface reconstruction algorithm consists of computing an implicit function which is an approximate indicator function of the inferred solid (Poisson Surface Reconstruction - referred to as Poisson). Poisson is a two steps process: it requires solving for the implicit function before function evaluation.
Surface reconstruction from point sets is often a sequential process with the following steps: 1) Scanning and scan alignment produce a set of points or points with normals; 2) Outlier removal; 3) Simplification to reduce the number of input points; 4) Smoothing to reduce noise in the input data; 5) Normal estimation and orientation when the normals are not already provided by the acquisition device; and 6) Surface reconstruction.
Cgal provides algorithms for all steps listed above except alignment.
Chapter Point_set_processing_3 58 describes algorithms to pre-process the point set before reconstruction with functions devoted to the simplification, outlier removal, smoothing, normal estimation and normal orientation.
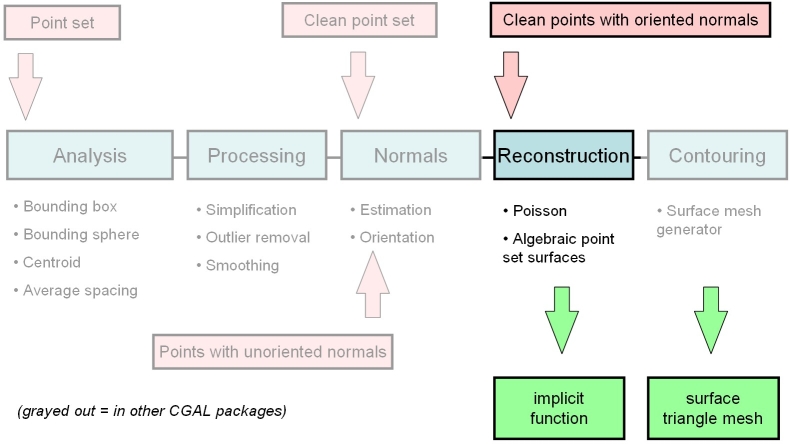
Given a set of 3D points with oriented normals (denoted oriented points in the sequel) sampled on the boundary of a 3D solid, the Poisson Surface Reconstruction method [KBH06] solves for an approximate indicator function of the inferred solid, whose gradient best matches the input normals. The output scalar function, represented in an adaptive octree, is then iso-contoured using an adaptive marching cubes.
Cgal implements a variant of this algorithm which solves for a piecewise linear function on a 3D Delaunay triangulation instead of an adaptive octree. The algorithm takes as input a set of 3D oriented points. It builds a 3D Delaunay triangulation from these points and refines it by Delaunay refinement so as to remove all badly shaped (non isotropic) tetrahedra and to tessellate a loose bounding box of the input oriented points. The normal of each Steiner point added during refinement is set to zero. It then solves for a scalar indicator function f represented as a piecewise linear function over the refined triangulation. More specifically, it solves for the Poisson equation Δf = div(n) at each vertex of the triangulation using a sparse linear solver. Eventually, the Cgal surface mesh generator extracts an isosurface with function value set by default to be the median value of f at all input points.
The class template declaration is:
template<
class Gt>
class Poisson_reconstruction_function;
with
Gt: Geometric traits class.
Creation:
| template<typename InputIterator, typename PointPMap, typename NormalPMap> | ||||||
| ||||||
Creates a Poisson implicit function from the [first, beyond) range of points.
| ||||||
The main operations are:
| Sphere | bounding_sphere () const | Returns a sphere bounding the inferred surface. |
| bool | compute_implicit_function () |
The function compute_implicit_function() must be called after each insertion of oriented points. It computes the piecewise linear scalar function operator() by: applying Delaunay refinement, solving for operator() at each vertex of the triangulation with a sparse linear solver, and shifting and orienting operator() such that it is 0 at all input points and negative inside the inferred surface. Returns false if the linear solver fails. The sparse solver used for this step is a parameter of the function. We recommend to use the class CGAL::Eigen_solver_traits<T> instantiated with the iterative conjugate gradient solver Eigen::ConjugateGradient for double (which is the default when Eigen is available and CGAL_EIGEN3_ENABLED is defined). |
| FT | value ( Point p) const | Evaluates the implicit function at a given 3D query point. |
| Point | get_inner_point () const | Returns an arbitrary point located inside the inferred surface. |
See details in
CGAL::Poisson_reconstruction_function<GeomTraits>
poisson_reconstruction_example.cpp reads a point set, creates a Poisson implicit function and reconstructs a surface.
File: examples/Surface_reconstruction_points_3/poisson_reconstruction_example.cpp
#include <CGAL/trace.h>
#include <CGAL/Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel.h>
#include <CGAL/Polyhedron_3.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/Polyhedron_iostream.h>
#include <CGAL/Surface_mesh_default_triangulation_3.h>
#include <CGAL/make_surface_mesh.h>
#include <CGAL/Implicit_surface_3.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/output_surface_facets_to_polyhedron.h>
#include <CGAL/Poisson_reconstruction_function.h>
#include <CGAL/Point_with_normal_3.h>
#include <CGAL/property_map.h>
#include <CGAL/IO/read_xyz_points.h>
#include <CGAL/compute_average_spacing.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
// Types
typedef CGAL::Exact_predicates_inexact_constructions_kernel Kernel;
typedef Kernel::FT FT;
typedef Kernel::Point_3 Point;
typedef CGAL::Point_with_normal_3<Kernel> Point_with_normal;
typedef Kernel::Sphere_3 Sphere;
typedef std::vector<Point_with_normal> PointList;
typedef CGAL::Polyhedron_3<Kernel> Polyhedron;
typedef CGAL::Poisson_reconstruction_function<Kernel> Poisson_reconstruction_function;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh_default_triangulation_3 STr;
typedef CGAL::Surface_mesh_complex_2_in_triangulation_3<STr> C2t3;
typedef CGAL::Implicit_surface_3<Kernel, Poisson_reconstruction_function> Surface_3;
int main(void)
{
// Poisson options
FT sm_angle = 20.0; // Min triangle angle in degrees.
FT sm_radius = 30; // Max triangle size w.r.t. point set average spacing.
FT sm_distance = 0.375; // Surface Approximation error w.r.t. point set average spacing.
// Reads the point set file in points[].
// Note: read_xyz_points_and_normals() requires an iterator over points
// + property maps to access each point's position and normal.
// The position property map can be omitted here as we use iterators over Point_3 elements.
PointList points;
std::ifstream stream("data/kitten.xyz");
if (!stream ||
!CGAL::read_xyz_points_and_normals(
stream,
std::back_inserter(points),
CGAL::make_normal_of_point_with_normal_pmap(std::back_inserter(points))))
{
std::cerr << "Error: cannot read file data/kitten.xyz" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Creates implicit function from the read points using the default solver.
// Note: this method requires an iterator over points
// + property maps to access each point's position and normal.
// The position property map can be omitted here as we use iterators over Point_3 elements.
Poisson_reconstruction_function function(
points.begin(), points.end(),
CGAL::make_normal_of_point_with_normal_pmap(points.begin()));
// Computes the Poisson indicator function f()
// at each vertex of the triangulation.
if ( ! function.compute_implicit_function() )
return EXIT_FAILURE;
// Computes average spacing
FT average_spacing = CGAL::compute_average_spacing(points.begin(), points.end(),
6 /* knn = 1 ring */);
// Gets one point inside the implicit surface
// and computes implicit function bounding sphere radius.
Point inner_point = function.get_inner_point();
Sphere bsphere = function.bounding_sphere();
FT radius = std::sqrt(bsphere.squared_radius());
// Defines the implicit surface: requires defining a
// conservative bounding sphere centered at inner point.
FT sm_sphere_radius = 5.0 * radius;
FT sm_dichotomy_error = sm_distance*average_spacing/1000.0; // Dichotomy error must be << sm_distance
Surface_3 surface(function,
Sphere(inner_point,sm_sphere_radius*sm_sphere_radius),
sm_dichotomy_error/sm_sphere_radius);
// Defines surface mesh generation criteria
CGAL::Surface_mesh_default_criteria_3<STr> criteria(sm_angle, // Min triangle angle (degrees)
sm_radius*average_spacing, // Max triangle size
sm_distance*average_spacing); // Approximation error
// Generates surface mesh with manifold option
STr tr; // 3D Delaunay triangulation for surface mesh generation
C2t3 c2t3(tr); // 2D complex in 3D Delaunay triangulation
CGAL::make_surface_mesh(c2t3, // reconstructed mesh
surface, // implicit surface
criteria, // meshing criteria
CGAL::Manifold_with_boundary_tag()); // require manifold mesh
if(tr.number_of_vertices() == 0)
return EXIT_FAILURE;
// saves reconstructed surface mesh
std::ofstream out("kitten_poisson-20-30-0.375.off");
Polyhedron output_mesh;
CGAL::output_surface_facets_to_polyhedron(c2t3, output_mesh);
out << output_mesh;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
The surface reconstruction problem being inherently ill-posed, the proposed algorithm does not pretend to reconstruct all kinds of surfaces with arbitrary sampling conditions. This section provides the user with some hints about the ideal sampling and contouring conditions, and depicts some failure cases when these conditions are not matched.
The user must keep in mind that the poisson surface reconstruction algorithm comprises two phases (computing the implicit function from the input point set and contouring an iso-surface of this function). Both require some care in terms of sampling conditions and parameter tuning.
Ideally the current implementation of the Poisson surface reconstruction method expects a dense 3D oriented point set (typically matching the epsilon-sampling condition [BO05]) and sampled over a closed, smooth surface. Oriented herein means that all 3D points must come with consistently oriented normals to the inferred surface. Figures 49.3 and 49.4 illustrate cases where these ideal conditions are met.
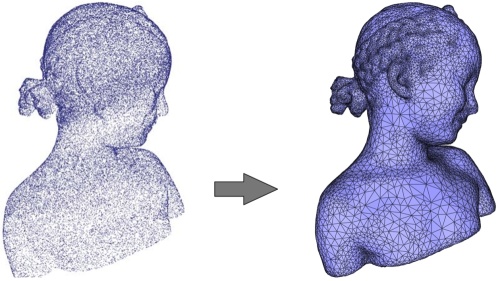
Figure 49.3: Poisson reconstruction. Left: 120K points sampled on a statue (Minolta laser scanner). Right: reconstructed surface mesh.
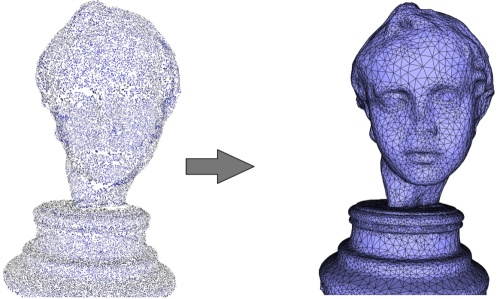
Figure 49.4: Left: 120K points sampled on a statue (Minolta laser scanner). Right: reconstructed surface mesh.
The algorithm is fairly robust to anisotropic sampling and to noise. It is also robust to missing data through filling the corresponding holes as the algorithm is designed to reconstruct the indicator function of an inferred solid (see Figure 49.5).
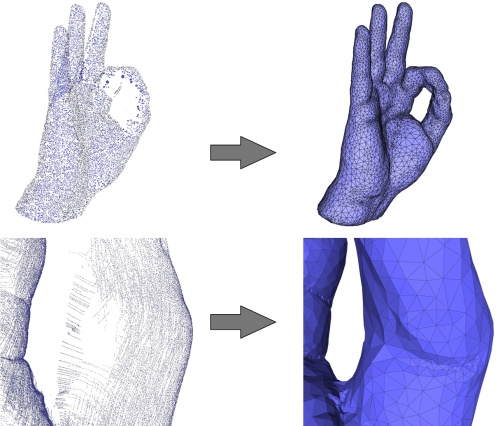
Figure 49.5: Top left: 65K points sampled on a hand (Kreon laser scanner). Bottom left: the point set is highly anisotropic due to the scanning technology. Right: reconstructed surface mesh and closeup. The holes are properly closed.
The algorithm is in general not robust to outliers, although a few outliers do not always create a failure, see Figure 49.6.
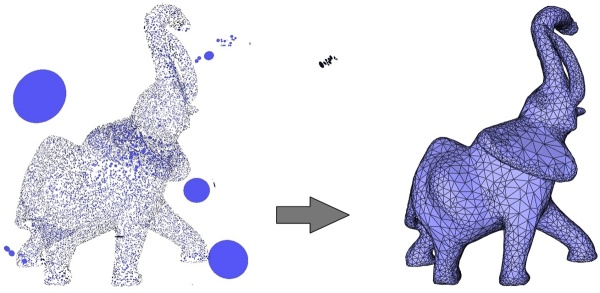
Figure 49.6: Left: 70K points sampled on an elephant with few outliers emphasized with disks. Right: reconstructed surface mesh.
The algorithm works well even when the inferred surface is composed of several connected components, provided that both all normals are properly estimated and oriented (the current Cgal normal orienter algorithm may fail in some cases, see CGAL::mst_orient_normals()), and that the final contouring algorithm is properly seeded for each component. When the inferred surface is composed of several nested connected components care should be taken to orient the normals of each component in alternation (inward/outward) so that the final contouring stage picks a proper contouring value.
Our implementation of the Poisson surface reconstruction algorithm computes an implicit function represented as a piecewise linear function over the tetrahedra of a 3D Delaunay triangulation constructed from the input points then refined through Delaunay refinement. For this reason, any iso-surface is also piecewise linear and hence may contain sharp creases. As the contouring algorithm CGAL::make_surface_mesh() expects a smooth implicit function these sharp creases may create spurious clusters of vertices in the final reconstructed surface mesh when setting a small mesh sizing or surface approximation error parameter (see Figure 49.7).
One way to avoid these spurious clusters consists of adjusting the mesh sizing and surface approximation parameters large enough compared to the average sampling density (obtained through CGAL::compute_average_spacing()) so that the contouring algorithm ``perceives'' a smooth iso-surface. We recommend to use the following contouring parameters:
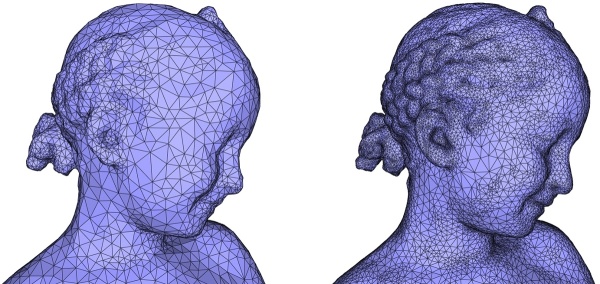
Figure 49.7: Left: surface reconstructed with approximation distance = 0.25 * average spacing. Right: surface reconstructed with approximation distance = 0.15 * average spacing. Notice the spurious cluster on the chick.
The conditions listed above are rather restrictive and in practice not all of them are met in the applications. We now illustrates the behavior of the algorithm when the conditions are not met in terms of sampling, wrongly oriented normals, noise and sharp creases.
The reconstruction algorithm expects a sufficiently dense point set. Although there is no formal proof of correctness of the algorithm under certain density conditions due to its variational nature, our experiments show that the algorithm reconstructs well all thin features when the local spacing is at most one tenth of the local feature size (the distance to the medial axis, which captures altogether curvature, thickness and separation). When this condition is not met the reconstruction does not reconstruct the thin undersampled features (see Figure 49.8).
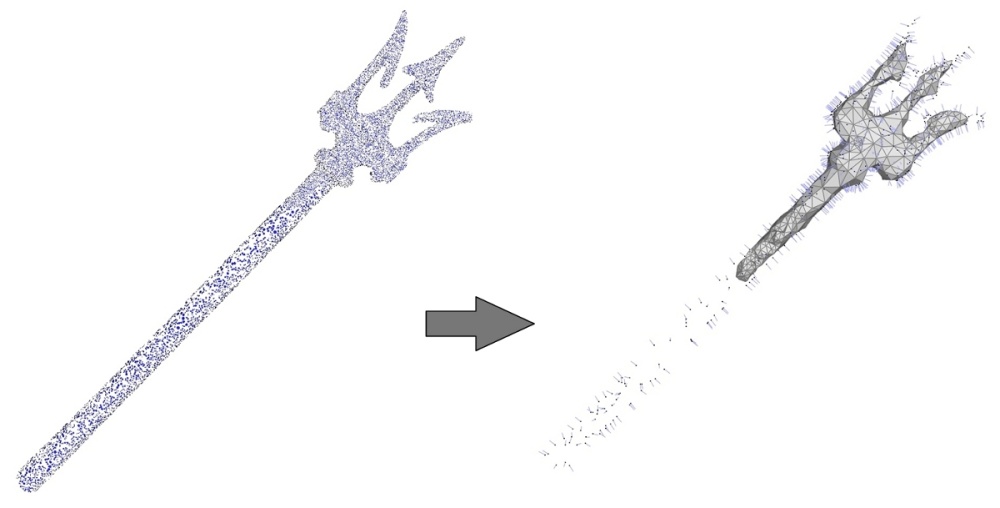

Figure 49.8: Left: 50K points sampled on the Neptune trident. The reconstruction (not shown) is successful in this case. Right: point set simplified to 1K points then reconstructed (all input points are depicted with normals). The thin feature is not reconstructed.
The reconstruction is devised to solve for an implicit function which is an approximate indicator function of an inferred solid. For this reason the contouring algorithm always extracts a closed surface mesh and hence is able to fill the small holes where data are missing due, e.g., to occlusions during acquisition. In case of large holes the algorithm still closes them all but sometimes in an unexpected manner. In addition the resulting piecewise linear implicit function may exhibit large triangle patches and sharp creases as the 3D Delaunay triangulation used for solving is very coarse where the holes are filled (see Figure 49.9).
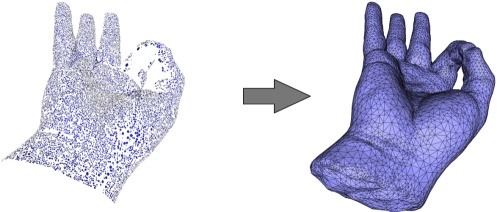
Figure 49.9: Left: 65K points sampled on a hand with no data captured at the wrist base. Right: reconstructed surface mesh. The surface is properly closed on the fingers and also closed at the wrist but in a less plausible manner.
The Poisson surface reconstruction approaches solves for an implicit function whose gradient best matches a set of input normals. Because it solves this problem in the least squares sense, it is robust to few isolated wrongly oriented (flipped) normals. Nevertheless a cluster of wrongly oriented normals leads to an incorrect implicit function and hence to spurious geometric or even topological distortion (see Figure 49.10).
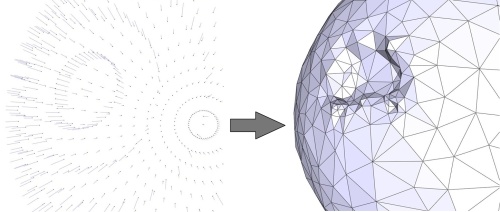
Figure 49.10: Left: points sampled on a sphere with a cluster of wrongly oriented normals. Right: reconstructed surface mesh with a spurious bump.
A large amount of noise inevitably impacts on the reconstruction (see Figure 49.11, top) and the current implementation does not provide any mean to trade data fitting for smoothness. Nevertheless if the signal-to-noise ratio is sufficiently high and/or the surface approximation and sizing parameters set for contouring the iso-surface is large with respect to the noise level the output surface mesh will appear smooth (not shown). If the user wants to produce a smooth and detailed output surface mesh, we recommend to apply smoothing through CGAL::jet_smooth_point_set() ((see Figure 49.11, bottom).
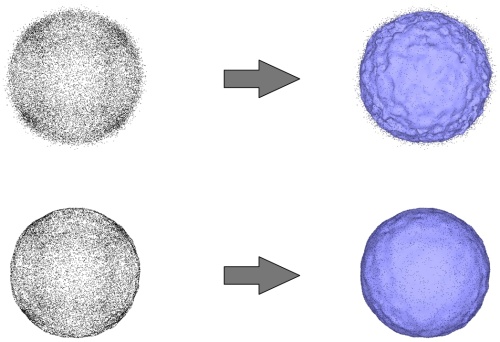
Figure 49.11: Top-left: points sampled on a sphere and corrupted with a lot of noise. Top-right: reconstructed surface mesh. Bottom-left: smoothed point set. Bottom-right: reconstructed surface mesh.
For a large number of outliers the failure cases (not shown) translate into spurious small connected components and massive distortion near the inferred surface. In this case the outliers must be removed through CGAL::remove_outliers().
The current reconstruction algorithm is not able to recover the sharp creases and corners present in the inferred surface. This translates into smoothed sharp creases.
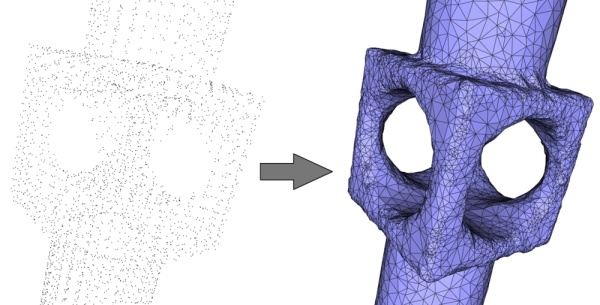
Figure 49.12: Left: 5K points sampled on a mechanical piece with sharp features (creases, darts and corners). Right: reconstructed surface mesh with smoothed creases.